Time Series Forecasting
Contents
Time Series Forecasting#
Summary#
Using all recorded annual temperatures averages (from 1850 to 2020), I use Prophet to forecast annual temperatures for the next two decades.
Data Source#
Average northern hemisphere temperature data was obtained from https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadcrut5/, specifically the “HadCRUT5 analysis time series: ensemble means and uncertainties”. The temperatures are expressed as deviations, or anomalies, from reference temperatures over the period of 1961–1990; for details see here. Each anomaly is a best estimate calculated from an ensemble of 100 time series, hence confidence intervals are present in the dataset. For the purposes of this analysis, I will just use the point estimate.
Data Exploration#
Let’s load in the data and examine it:
Note
You can run and modify the code on this page Jupyter Notebook style, but without leaving the page! Hover over the launch button at the top of the page, then click the Live Code button. If you prefer a Jupyter environment, use the Binder button instead.
You’ll need to run the following cell manually because Live Code sessions assume a cwd of the root directory.
Refresh the page to revert to the original view.
import os
try:
os.chdir("./website/stat-ml/")
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
print(f"cwd: {os.getcwd()}")
cwd: /home/adam/projects/website/website/stat-ml
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("./globwarm.csv")
df.head(3)
| Time | Anomaly (deg C) | Lower confidence limit (2.5%) | Upper confidence limit (97.5%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1850 | -0.435791 | -0.635680 | -0.235902 |
| 1 | 1851 | -0.219249 | -0.428398 | -0.010100 |
| 2 | 1852 | -0.235702 | -0.457689 | -0.013715 |
df.tail(3)
| Time | Anomaly (deg C) | Lower confidence limit (2.5%) | Upper confidence limit (97.5%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 169 | 2019 | 1.143743 | 1.108290 | 1.179197 |
| 170 | 2020 | 1.275727 | 1.236863 | 1.314590 |
| 171 | 2021 | 1.004906 | 0.764207 | 1.245604 |
Since 2021 data collection is still ongoing, the confidence limits are much wider. For simplicity, I’ll drop this point from the analysis.
df = df[df.Time <= 2020]
Next, let’s plot the data:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(df.Time, df["Anomaly (deg C)"], "o")
ax.set(xlabel="Year", ylabel="Temperature (C)")
plt.show()
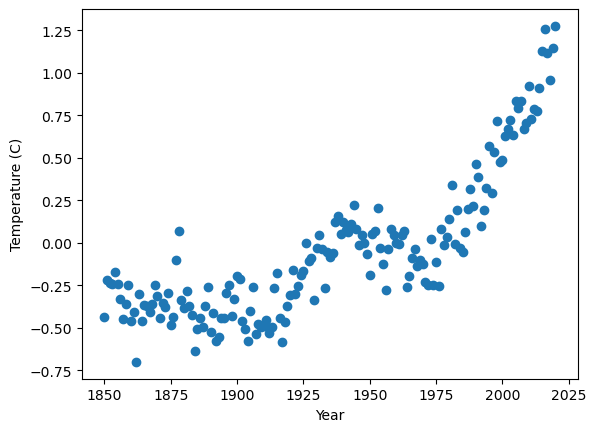
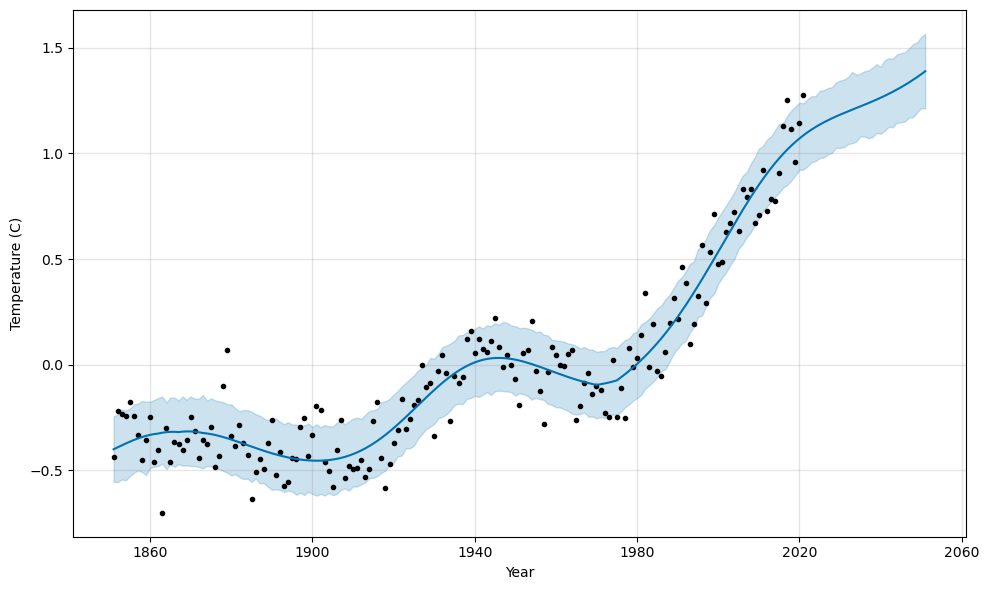
There is also clearly a nonlinear trend amidst the random variation from year to year. We also expect some long term cyclical patterns, for instance Milankovitch cycles due to variations in Earth’s movement relative to the Sun. However, these patterns are difficult to extract because we have just under 200 years of data to work with. These cyclical patterns are very important, however, because we don’t have access to more granular data with daily, weekly, and/or yearly variation typically present in business problems. For this reason, Prophet is useful as it can easily implement custom seasonalities. It’s also flexible in its ability to detect changepoints, another crucial parameter affecting model fit as we will see next.
Building a Simple Forecast#
First, we must format the data appropriately.
Prophet expects a two column dataframe with datestamps ds formatted like YYYY-MM-DD and numeric data y.
def format_years(years):
"""Convert numeric years to YYYY-MM-DD format, using an arbitrary day."""
ds = [str(year) + "-12-31" for year in years]
return ds
df = df[["Time", "Anomaly (deg C)"]].rename(
columns={"Time": "ds", "Anomaly (deg C)": "y"}
)
df.ds = format_years(df.ds)
df.head(3)
| ds | y | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1850-12-31 | -0.435791 |
| 1 | 1851-12-31 | -0.219249 |
| 2 | 1852-12-31 | -0.235702 |
df.tail(3)
| ds | y | |
|---|---|---|
| 168 | 2018-12-31 | 0.959662 |
| 169 | 2019-12-31 | 1.143743 |
| 170 | 2020-12-31 | 1.275727 |
df is now ready for Prophet modeling, but as hinted in § Data Exploration, a model built from defaults performs very poorly:
from prophet import Prophet
def plot_model_fit(model, df):
"""Fit and plot predictions of a Prophet() model on the training data."""
model.fit(df)
predictions = model.predict()
model.plot(predictions, xlabel="Year", ylabel="Temperature (C)")
model = Prophet()
plot_model_fit(model, df)
Importing plotly failed. Interactive plots will not work.
INFO:prophet:Disabling weekly seasonality. Run prophet with weekly_seasonality=True to override this.
INFO:prophet:Disabling daily seasonality. Run prophet with daily_seasonality=True to override this.
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -17.5035
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
99 217.559 0.000640947 66.6814 1 1 128
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
188 218.511 0.00158703 88.0943 2.803e-05 0.001 286 LS failed, Hessian reset
199 218.616 5.91156e-05 56.8093 0.07449 1 306
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
292 218.705 2.68884e-05 64.9809 3.837e-07 0.001 470 LS failed, Hessian reset
299 218.705 5.18845e-06 67.2586 1 1 478
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
334 218.706 2.36909e-06 77.496 3.097e-08 0.001 563 LS failed, Hessian reset
342 218.706 1.90175e-09 66.7851 0.03287 0.03287 575
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
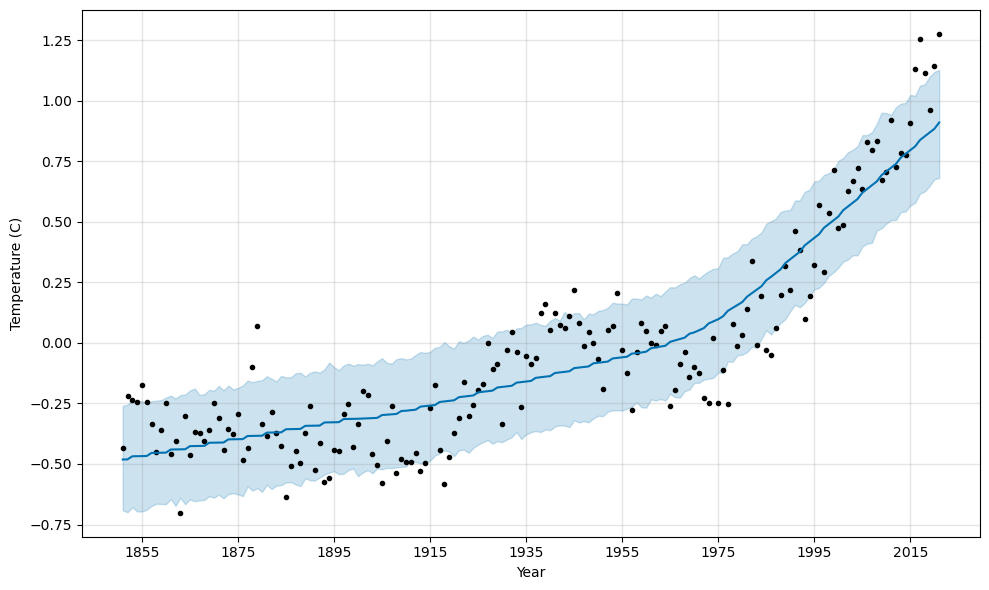
The reason is that we need to account for long term cycles over many years.
A yearly seasonality is meaningless in this context, because we don’t have sub-year level data.
Let’s try again, disabling the usual seasonalities and implementing our own using the add_seasonality() method.
From the scatterplot of the raw data, any noticeable variation occurs after at least 50 years.
At this scale, the variation is relatively small, so the fit shouldn’t be too flexible.
In other words, we shouldn’t include too many Fourier terms, controlled by the fourier_order parameter.
model = Prophet(
daily_seasonality=False,
weekly_seasonality=False,
yearly_seasonality=False,
)
model.add_seasonality("50 years", period=365 * 50, fourier_order=2)
plot_model_fit(model, df)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -17.5035
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
53 218.827 0.0054749 100.245 5.445e-05 0.001 94 LS failed, Hessian reset
86 219.303 0.000428905 65.8946 5.252e-06 0.001 191 LS failed, Hessian reset
99 219.314 7.47284e-06 41.2342 0.5794 0.5794 211
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
160 219.835 0.000219902 48.0568 4.058e-06 0.001 343 LS failed, Hessian reset
193 219.863 0.000114599 67.8428 1.766e-06 0.001 422 LS failed, Hessian reset
199 219.865 2.8985e-06 48.9324 0.2933 0.2933 429
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
219 219.866 1.76065e-06 49.44 3.818e-08 0.001 492 LS failed, Hessian reset
234 219.866 9.82303e-09 50.957 0.09921 0.09921 514
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
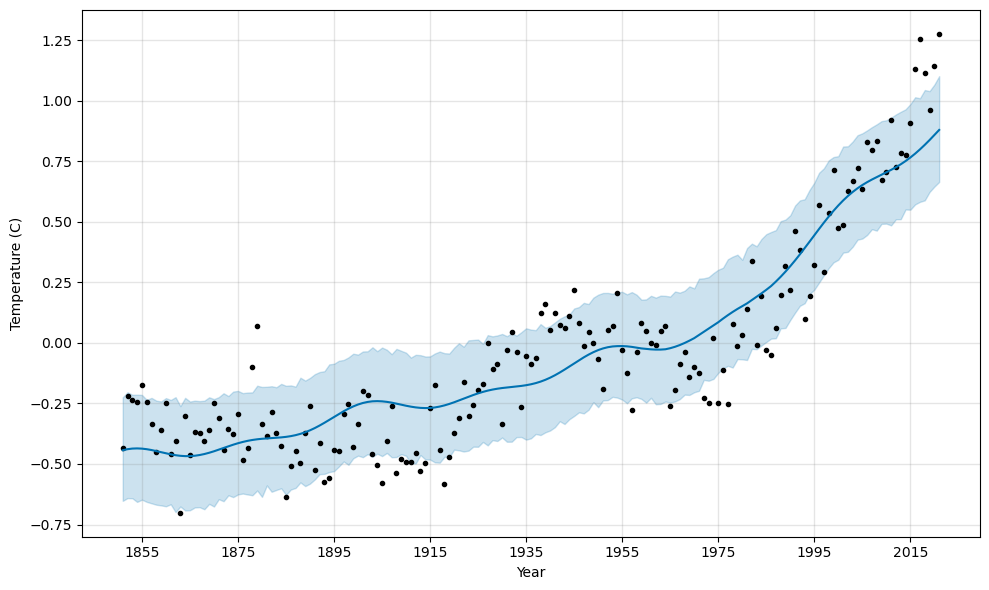
The fit’s a bit better in terms of smoothness, but still not great.
Increasing fourier_order just amounts to more more variation around a similar mean trend line.
Let’s try increasing the seasonality period a bit more:
model = Prophet(
daily_seasonality=False,
weekly_seasonality=False,
yearly_seasonality=False,
)
model.add_seasonality("centuryly", period=365 * 100, fourier_order=2)
plot_model_fit(model, df)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -17.5035
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
95 248.116 5.36108e-05 42.8226 8.505e-07 0.001 168 LS failed, Hessian reset
99 248.117 5.87883e-06 49.9379 0.8928 0.08928 175
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
158 248.125 4.68896e-07 57.519 8.193e-09 0.001 306 LS failed, Hessian reset
163 248.125 8.11851e-09 51.7867 0.1544 0.1544 312
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
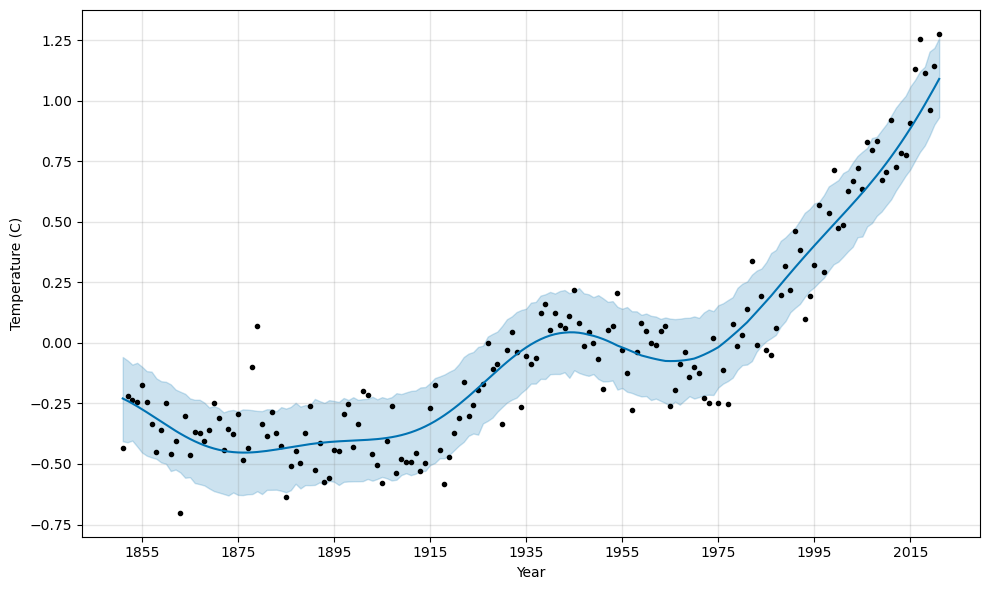
The fit is much better. Let’s see what it forecasts.
future = model.make_future_dataframe(periods=30, freq="Y")
forecast = model.predict(future)
model.plot(forecast, xlabel="Year", ylabel="Temperature (C)")
plt.show()
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
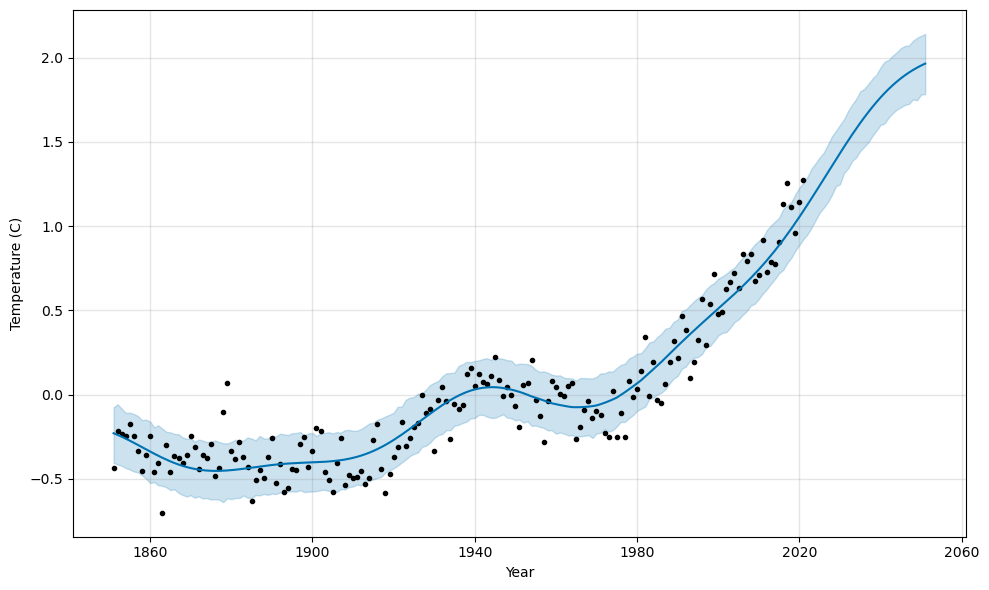
The model stays roughly linear with the latest data, but levels off due to the seasonality built into the model.
Optimizing the Forecast#
The previous hand-tuning was insightful, but largely experimental. A more principled approach tunes the parameters based on some performance metric(s). Cross-validation is often used for this, but we have to be a bit careful with time series data due to correlations between data points. One approach preserves the ordering of time by training on the first (say) 100 years of data and testing on the next 20 years of data. Then we train on the first 110 years of data and again test on the next 20 years of data. We repeat this until we reach the end of the data. Each batch gives us an estimate of errors of predictions made 1, 2, …, 20 years in the future while preserving the ordering of time. This approach can be implemented in Prophet as follows:
from prophet.diagnostics import cross_validation
df_cv = cross_validation(model, initial="36500 days", horizon="7300 days")
df_cv.head(3)
INFO:prophet:Making 6 forecasts with cutoffs between 1951-01-18 00:00:00 and 2001-01-05 00:00:00
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -5.25924
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
75 127.229 9.68385e-10 101.584 0.09599 0.09599 96
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -5.36242
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
99 139.461 9.76843e-05 103.123 0.7929 0.7929 120
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
143 139.524 4.58751e-05 102.166 4.693e-07 0.001 204 LS failed, Hessian reset
168 139.527 7.1662e-09 100.937 0.1476 0.1476 239
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -5.73025
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
99 153.794 3.71888e-06 105.159 0.349 1 126
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
138 153.795 7.36488e-09 106.455 0.4683 0.4683 176
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -6.64014
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
82 164.752 0.000308592 101.842 3.108e-06 0.001 141 LS failed, Hessian reset
99 164.769 1.70261e-06 99.5116 0.5224 0.5224 162
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
117 164.769 8.94213e-09 99.2085 0.177 0.177 184
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -14.1508
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
88 163.574 0.001071 107.114 9.956e-06 0.001 160 LS failed, Hessian reset
99 163.666 0.000165312 102.358 0.9734 0.9734 172
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
182 163.726 6.51677e-09 95.6481 0.2608 0.2608 276
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -12.6326
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
99 151.557 4.53253e-06 54.8127 0.5863 0.5863 139
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
174 151.578 5.73067e-05 84.3149 7.726e-07 0.001 277 LS failed, Hessian reset
199 151.58 2.07059e-07 47.3968 0.3915 0.3915 310
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
232 151.58 6.29633e-09 67.7881 0.2082 1 358
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: absolute parameter change was below tolerance
| ds | yhat | yhat_lower | yhat_upper | y | cutoff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1951-12-31 | -0.006353 | -0.166391 | 0.143413 | 0.053849 | 1951-01-18 |
| 1 | 1952-12-31 | -0.015820 | -0.169072 | 0.145026 | 0.069817 | 1951-01-18 |
| 2 | 1953-12-31 | -0.025520 | -0.173296 | 0.125185 | 0.206579 | 1951-01-18 |
df_cv.tail(3)
| ds | yhat | yhat_lower | yhat_upper | y | cutoff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 117 | 2018-12-31 | 0.104307 | -0.092542 | 0.308903 | 0.959662 | 2001-01-05 |
| 118 | 2019-12-31 | 0.115870 | -0.081466 | 0.311119 | 1.143743 | 2001-01-05 |
| 119 | 2020-12-31 | 0.129318 | -0.085928 | 0.320792 | 1.275727 | 2001-01-05 |
For example, we see the the first cutoff point is in 1960.
The model is trained on data up until the cutoff, then predictions (yhat) are made for the next 20 years.
The cutoff points are then incremented by 10 years until 2000.
I’ll measure model performance using mean squared error (MSE), but a variety of metrics could be used.
We can plot MSE as a function of horizon length (how far in time the prediction is made) using plot_cross_validation_metric();
unsurprisingly, performance is worse the farther out the window:
from prophet.plot import plot_cross_validation_metric
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
plot_cross_validation_metric(df_cv, metric="mse", rolling_window=0.1, ax=ax, color="C0")
plot_cross_validation_metric(df_cv, metric="mse", rolling_window=0.5, ax=ax, color="C1")
plt.show()
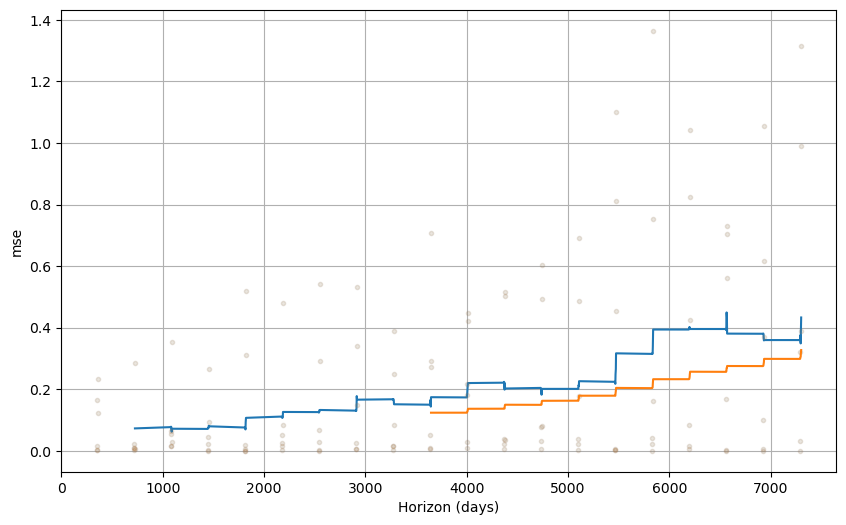
The two curves differ by the amount of averaging used in computing the MSE.
Each point in the blue curved is averaged over 10% of the data while the orange curve is averaged over 50% of the data.
The blue curve is more variable but can give estimates over shorter horizons.
Setting rolling_window=1 averages over all the data, giving just a single average estimate for the MSE predicting within a 20 year horizon.
A dataframe of metrics can be extracted with performance_metrics():
from prophet.diagnostics import performance_metrics
df_performance = performance_metrics(df_cv, rolling_window=1)
df_performance
| horizon | mse | rmse | mae | mape | mdape | smape | coverage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 7300 days | 0.225348 | 0.474709 | 0.358713 | 3.293734 | 1.071312 | 1.544548 | 0.383333 |
The above code with rolling_window=1 is useful for hyperparameter tuning.
It allows us to optimizing average performance over a fixed horizon window.
This is done in the code below to find the optimum seasonality period and number of Fourier terms.
I also optimize over two model parameters changepoint_prior_scale and seasonality_prior_scale which control the flexibility of the changepoints and seasonalities.
import itertools
def make_grid_combinations(grid):
"""Turn a dictionary of grid points into a dictionary of all combinations
of those grid points."""
all_params = []
for vals in itertools.product(*grid.values()):
all_params.append(dict(zip(grid.keys(), vals)))
return all_params
param_grid = {
'period': [50, 75, 100],
'fourier_order': [2, 4, 6],
'changepoint_prior_scale': [.005, .05, .5],
'seasonality_prior_scale': [.1, 1, 10],
}
all_params = make_grid_combinations(param_grid)
mses = []
# Cross-validate each combination of grid parameters to estimate MSEs
for params in all_params:
model = Prophet(
daily_seasonality = False,
weekly_seasonality = False,
yearly_seasonality = False,
changepoint_prior_scale = params['changepoint_prior_scale'],
seasonality_prior_scale = params['seasonality_prior_scale']
)
model.add_seasonality(
name = str(params['period']) + ' year',
period = 365 * params['period'],
fourier_order = params['fourier_order']
)
model.fit(df)
df_cv = cross_validation(model, initial='36500 days', horizon='7300 days')
df_performance = performance_metrics(df_cv, rolling_window=1)
mses.append(df_performance['mse'].values[0])
tuning_results = pd.DataFrame(all_params)
tuning_results['mse'] = mses
tuning_results.to_csv('tuning_results.csv', index=False)
The result is stored in a dataframe of cross-validated MSEs and the parameters used in the model:
tuning_results = pd.read_csv("./tuning_results.csv")
tuning_results
| period | fourier_order | changepoint_prior_scale | seasonality_prior_scale | mse | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50 | 2 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.154416 |
| 1 | 50 | 2 | 0.005 | 1.0 | 0.155571 |
| 2 | 50 | 2 | 0.005 | 10.0 | 0.156148 |
| 3 | 50 | 2 | 0.050 | 0.1 | 0.152661 |
| 4 | 50 | 2 | 0.050 | 1.0 | 0.154947 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 76 | 100 | 6 | 0.050 | 1.0 | 0.243489 |
| 77 | 100 | 6 | 0.050 | 10.0 | 0.245329 |
| 78 | 100 | 6 | 0.500 | 0.1 | 0.108537 |
| 79 | 100 | 6 | 0.500 | 1.0 | 0.108298 |
| 80 | 100 | 6 | 0.500 | 10.0 | 0.106562 |
81 rows × 5 columns
The best parameters, measured by MSE, are easily obtained:
import numpy as np
best_params = tuning_results.iloc[np.argmin(tuning_results["mse"]), :]
best_params
period 75.000000
fourier_order 2.000000
changepoint_prior_scale 0.500000
seasonality_prior_scale 10.000000
mse 0.048304
Name: 35, dtype: float64
Let’s see what the optimized model looks like:
model = Prophet(
daily_seasonality=False,
weekly_seasonality=False,
yearly_seasonality=False,
changepoint_prior_scale=0.5,
seasonality_prior_scale=10.0,
)
model.add_seasonality("centuryly", period=365 * 75, fourier_order=2)
model.fit(df)
future = model.make_future_dataframe(periods=30, freq="Y")
forecast = model.predict(future)
model.plot(forecast, xlabel="Year", ylabel="Temperature (C)")
plt.show()
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
/home/adam/projects/website/env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/prophet/forecaster.py:896: FutureWarning: The frame.append method is deprecated and will be removed from pandas in a future version. Use pandas.concat instead.
components = components.append(new_comp)
Initial log joint probability = -17.5035
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
99 302.408 0.00570823 11.3782 1 1 120
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
119 303.216 0.000781285 20.5453 2.855e-05 0.001 185 LS failed, Hessian reset
199 304.138 7.30153e-05 7.3618 0.4801 0.4801 290
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
272 304.446 0.000393317 11.4501 2.713e-05 0.001 419 LS failed, Hessian reset
299 304.522 0.000217305 7.42838 0.3201 0.3201 452
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
346 304.735 0.00183216 21.7699 0.0001859 0.001 537 LS failed, Hessian reset
399 304.865 0.000122705 8.81822 0.3029 1 608
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
448 304.947 0.000699382 14.9056 8.463e-05 0.001 714 LS failed, Hessian reset
499 304.979 2.88487e-05 7.75454 0.3058 0.3058 774
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
551 304.984 0.000253777 7.0285 3.633e-05 0.001 887 LS failed, Hessian reset
599 304.986 9.19244e-06 7.14222 1 1 950
Iter log prob ||dx|| ||grad|| alpha alpha0 # evals Notes
602 304.986 1.93406e-05 6.94598 2.726e-06 0.001 992 LS failed, Hessian reset
625 304.986 3.04125e-07 6.87252 0.4057 1 1021
Optimization terminated normally:
Convergence detected: relative gradient magnitude is below tolerance